Master Program ( 4 - sections )
Interpersonal Skill Training
Interpersonal Skill Training
Interpersonal skills foster effective communication, collaboration, and conflict resolution in personal and professional settings

Our courses focus on building analytical and strategic abilities
Learn business communication, feedback handling & report writing.
Develop tactics for successful negotiations and managing disputes.
Foster strong teamwork, leadership, and group cohesion.
Enhance interpersonal interactions through empathy & tolerance.
Course Contents
Section 1 - Communication Skills
Communication is a two-way means of passing on information in the form of thoughts, opinions, and ideas between two or more individuals with the purpose of building an understanding. It involves sending and receiving messages through verbal and non-verbal methods
Duration – Approximately 4 Hours
Business communication: Feedback, emails, meetings, reports
Effective business communication ensures clarity and professionalism in workplace interactions. Providing constructive feedback helps individuals improve their performance while fostering a culture of continuous growth. Well-structured emails must be concise, clear, and professional to avoid misunderstandings and ensure efficient communication. Meetings should be organized with clear agendas and objectives, allowing participants to contribute meaningfully. Reports must present data, insights, and recommendations in a structured and persuasive manner to support decision-making
Group dynamics and brainstorming techniques
Understanding group dynamics is essential for effective teamwork, as different personalities and work styles impact collaboration. Successful brainstorming techniques, such as mind mapping, SCAMPER, and the nominal group technique, encourage creative problem-solving. Encouraging open participation ensures all voices are heard, leading to more innovative solutions. Effective facilitation skills help teams stay focused and extract valuable ideas while maintaining a positive group environment
Section 2 - Negotiation Skills
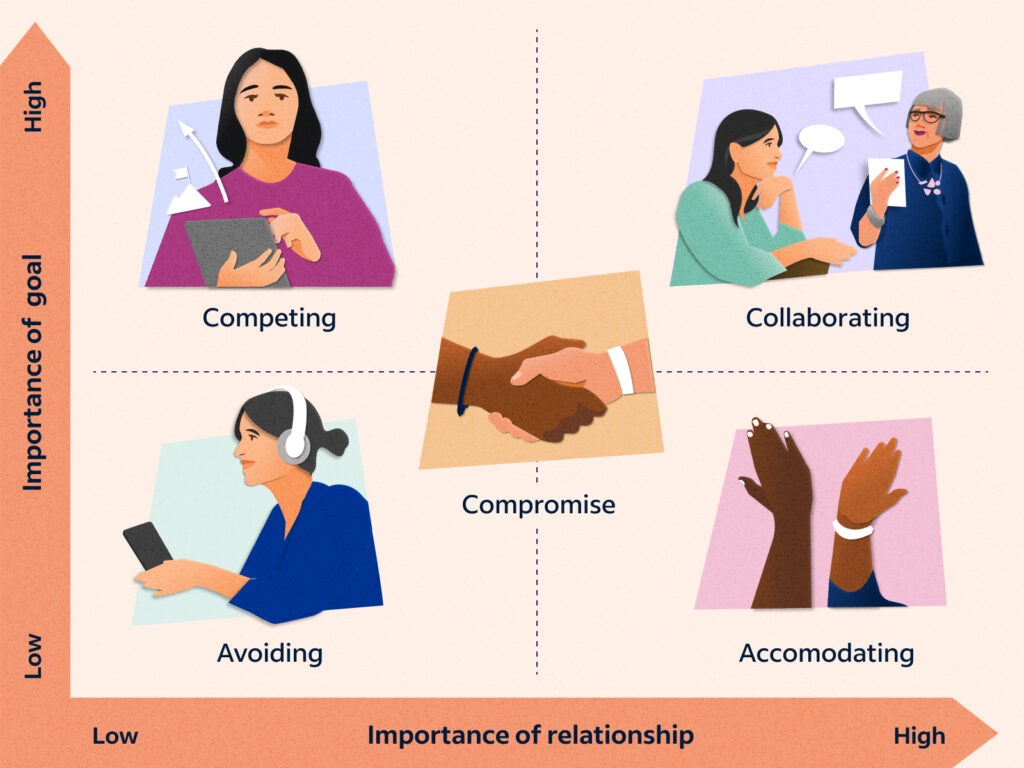
Negotiation is any form of direct or indirect communication during which the parties involved try to decide upon a mutually agreeable solution to the subject/topic/issue involved. The involved parties have something that the other party wants and during bargaining, reach to an agreeable outcome
Duration – Approximately 3 Hours

Body language interpretation
Non-verbal cues play a critical role in negotiations, often conveying more than spoken words. Facial expressions, posture, hand gestures, and eye contact can indicate confidence, hesitation, or discomfort. Learning to interpret these cues helps negotiators gauge the emotions and intentions of the other party. Mastering body language also involves controlling one’s own signals to appear composed, assertive, and trustworthy during discussions
Tactics for stalling and countering opponent strategies
Negotiation often involves strategic pauses or stalling to reassess positions and strengthen arguments. Deliberate stalling tactics, such as requesting additional information or deferring decisions, can provide time to develop stronger counterarguments. Countering opponent strategies requires awareness of persuasion techniques, such as anchoring, mirroring, and the “good cop, bad cop” approach. Successful negotiators recognize these strategies and respond with logic, data, and well-structured arguments to maintain a favorable position
Post-negotiation relationship management
Successful negotiations go beyond reaching an agreement—they also involve fostering long-term relationships. Following up with clear documentation, reiterating commitments, and expressing appreciation help solidify trust. Maintaining open communication post-negotiation ensures that agreements are upheld and any future issues are addressed collaboratively. Strong post-negotiation relationship management prevents disputes and strengthens professional partnerships for long-term success
Section 3 - Interpersonal Interactions
Building tolerance and active listening skills for harmonious relationships
Duration – Approximately 3 Hours
Developing empathy and patience
Empathy allows individuals to understand and connect with others by recognizing their emotions and perspectives. It fosters mutual respect, reduces conflicts, and strengthens both personal and professional relationships. Patience plays a crucial role in managing difficult situations, enabling individuals to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Cultivating empathy and patience enhances teamwork, leadership, and customer relations by creating a more inclusive and understanding environment
Techniques for effective listening
Active listening is more than just hearing words—it involves fully engaging with the speaker’s message, emotions, and intent. Techniques such as maintaining eye contact, paraphrasing key points, and asking clarifying questions help in demonstrating attentiveness. Avoiding distractions and practicing mindful listening build trust and encourage open dialogue. Strong listening skills lead to better decision-making, conflict resolution, and deeper interpersonal connections
Section 4 - Conflict Management
A conflict is a situation in which inacceptable differences in interests, expectations, values, and opinions occur in or between individuals or groups. Disagreements, discrepancies, and frictions that occur when the actions or beliefs of one or more members of the group are unacceptable to one or more other group members and are rejected by them. A state of tension that arises because there are irreconcilable contradictions between two or more parties regarding a certain good
Duration – Approximately 2 Hours
Root causes of conflict
Conflicts often arise due to miscommunication, clashing personalities, competing interests, or unaddressed grievances. Identifying these root causes helps in addressing the issue effectively rather than focusing solely on surface-level disagreements. Understanding emotional triggers, biases, and cultural differences prevents conflicts from escalating. Recognizing the underlying reasons behind conflicts allows for proactive resolution and the establishment of a more harmonious work environment
Strategies for de-escalation and resolution
De-escalation techniques, such as maintaining a calm tone, acknowledging emotions, and using neutral language, help diffuse tension before conflicts escalate. Conflict resolution strategies include collaborative problem-solving, compromise, and mediation to reach mutually beneficial outcomes. Encouraging open communication and active listening allows all parties to express concerns while working toward solutions. Effectively managing conflicts strengthens team dynamics and promotes a positive workplace culture
Section 5 - Team Building
Team building is a process that evolves the members into a cohesive group to reach to a common objective. The team members share their expectations for accomplishing group tasks, contribute to the tasks based on their competencies, build trust and support one another and respect one another’s individual differences.
Common goal, cohesion, collaboration, mutual respect are essential hallmarks of a good team
Duration – Approximately 3 Hours

Role of a leader in fostering collaboration
A leader plays a vital role in shaping team dynamics by setting a vision, encouraging open communication, and fostering a culture of collaboration. They must facilitate teamwork by assigning roles based on strengths, ensuring accountability, and motivating team members. Leaders who actively listen, provide support, and create an inclusive environment enhance team cohesion. Strong leadership promotes synergy, innovation, and efficiency within the team
Building trust and mutual respect
Trust and mutual respect are the foundation of strong teams, allowing members to rely on one another and collaborate effectively. Encouraging transparency, honesty, and fairness strengthens team bonds and enhances morale. Recognizing and valuing diverse perspectives helps create an inclusive team culture where individuals feel respected and heard. Building trust over time leads to higher engagement, increased productivity, and long-term team success
Key Objectives
Nature of Activities
- Classroom training on cognitive and interpersonal skills
- Orientation on Business Excellence, QMS, Lean, Operations Management, EMS, Financial Planning, etc
- Industry-focused training programs
- Interactive sessions between students and business experts
Training Methodology
- Classroom Training
- Group Dynamics
- Self-Reflection
- Video Analysis
- Group Interventions
- Feedback Discussions with Experts
