Master Program ( 5 - sections )
Cognitive Skills Training
Cognitive Skill Training
Cognitive skills empower individuals to think critically, solve problems innovate and be emotionally agile.

Our courses focus on building analytical and strategic abilities
Work on case studies and practical exercises for critical thinking
Master techniques like 8-D Methodology, Shainin System & FMEA
Apply analytical thinking, design thinking, and logical reasoning
Learn Design Thinking principles to develop human-centered solutions.
Course Contents
Section 1 - Emotional Intelligence (EI) & Emotional Agility
It involves recognizing and managing emotions in oneself and others. Emotional Agility, inspired by psychologist Susan David, emphasizes adaptability in emotional responses
Duration – Approximately 4 Hours

Pillars of EI: Self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, social skills
Emotional intelligence consists of key components that allow individuals to navigate both personal and professional relationships effectively. Self-awareness helps individuals recognize their emotions, while self-regulation enables them to control impulses. Motivation fuels persistence in challenging situations, while empathy and social skills enhance interpersonal interactions. Mastering these pillars contributes to stronger leadership, collaboration, and personal growth
Benefits of high EI: Improved relationships, leadership, and decision-making
Individuals with high emotional intelligence can communicate more effectively, manage conflicts with empathy, and build trust in relationships. Leaders with strong EI can inspire teams, resolve workplace tensions, and make informed, people-centered decisions. It also helps in stress management and maintaining a balanced perspective in difficult situations. Strong EI fosters adaptability and resilience, helping individuals navigate personal and professional challenges more effectively
Practical methods: Mindfulness, emotional literacy, growth mindset, value-based actions
Mindfulness enhances focus and self-awareness, allowing individuals to manage stress and emotions in real time. Emotional literacy helps in identifying and articulating emotions, improving both self-expression and understanding of others. A growth mindset encourages individuals to see challenges as learning opportunities rather than obstacles. Value-based actions guide decision-making and behavior, ensuring alignment with personal and professional goals
Handling emotionally challenging situations
Emotional challenges such as workplace conflicts, personal setbacks, or high-stress situations require effective coping mechanisms. Individuals can develop skills to manage difficult conversations, regulate their emotions under pressure, and respond to criticism constructively. Techniques such as reframing negative thoughts, seeking perspective, and engaging in active listening can significantly improve responses to challenges. Learning to regulate emotions in such situations enhances problem-solving skills and prevents impulsive reactions
Section 2 - Design Thinking
Design thinking is an iterative, non-linear process which focuses on collaboration between the designers and the users. It brings innovative solutions to life-based and how real users think, feel and behave.
Duration – Approximately 2 Hours
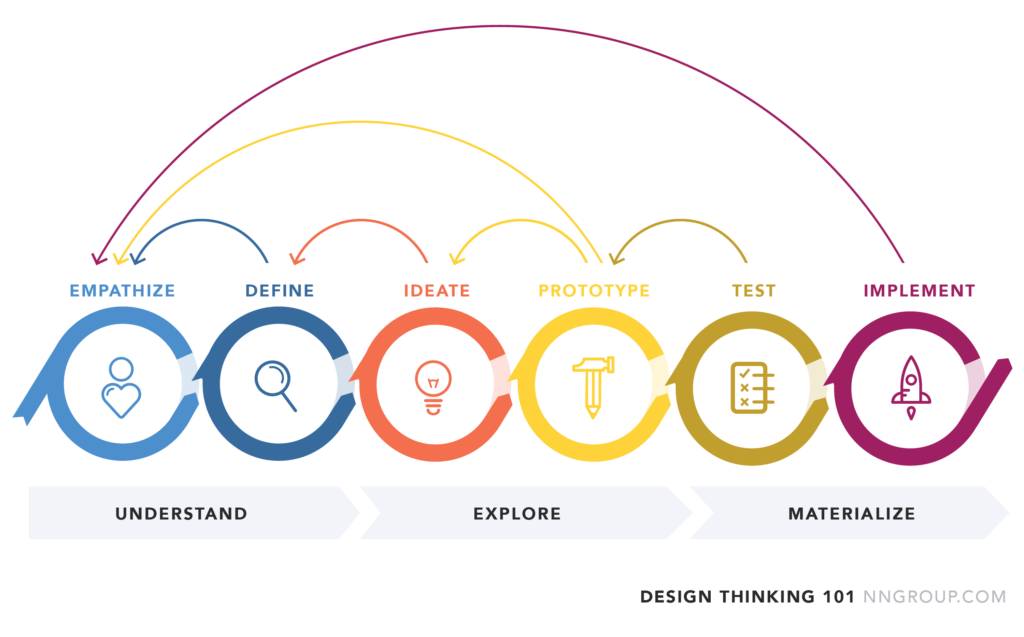
Core principles: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test
Design thinking follows a structured process that begins with understanding user needs and ends with implementing tested solutions. The empathy phase focuses on gathering deep insights about the problem, while defining helps in framing it correctly. Ideation involves brainstorming potential solutions, which are then turned into prototypes. The final testing phase ensures that the solution is refined and practical before full implementation
Applications in business and innovation.
Design thinking is widely used in industries such as technology, healthcare, education, and business strategy to develop user-friendly products and services. Companies apply it to enhance customer experience, create innovative solutions, and refine business models. It fosters creativity and helps organizations adapt to rapidly changing market demands. Many successful companies, including Apple and Google, integrate design thinking to develop groundbreaking products
Balancing desirability, feasibility, and viability
Effective design thinking ensures that solutions are desirable (meeting customer needs), feasible (technologically achievable), and viable (financially sustainable). A good idea must not only solve a problem but also be practical to execute within existing constraints. Businesses that achieve this balance can create long-lasting, innovative solutions that drive success. Understanding how to evaluate ideas based on these three aspects ensures efficient resource utilization and market acceptance
Section 3 - Problem Solving
Problem solving is the process of achieving a desired goal by addressing and overcoming obstacles in the process. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks to complex issues in business and technical fields.
Duration – Approximately 4 Hours
8-D Methodology
The 8-D (Eight Disciplines) methodology is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes identifying the root cause of an issue before implementing a solution. It includes defining the problem, forming a team, identifying and eliminating the root cause, and preventing recurrence. This method is widely used in manufacturing, quality control, and management to improve processes and resolve critical issues. By focusing on long-term solutions, the 8-D approach helps in preventing recurring problems
Shainin System
The Shainin System is a statistical problem-solving methodology used to identify variations and defects in processes. It relies on data-driven decision-making to pinpoint the root cause of a problem and eliminate inefficiencies. This system is particularly useful in engineering, manufacturing, and product development to enhance quality control and process optimization. By using statistical tools, it minimizes trial-and-error approaches and provides precise solutions
FMEA
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive risk assessment technique used to identify potential failures in a system or process. It involves evaluating failure modes, assessing their impact, and implementing preventive measures. Industries such as healthcare, aerospace, and automotive use FMEA to ensure safety and reliability. By addressing risks early, organizations can prevent costly failures and improve operational efficiency
6 Hat Thinking
The Six Thinking Hats method, developed by Edward de Bono, is a technique that encourages different perspectives when solving problems. Each “hat” represents a different way of thinking—facts, emotions, risks, benefits, creativity, and process control. This approach helps teams explore multiple viewpoints and avoid biases when making decisions. It is particularly effective in brainstorming sessions and strategic planning
Section 4 - Decision Making
Decision making is the process of choosing the best option from a set of possible choices. It involves identifying options, assessing their consequences, and selecting the best one
Duration – Approximately 2 Hours

Analytical reasoning
Analytical reasoning involves breaking down complex problems into smaller components for better understanding and evaluation. This skill enables individuals to assess multiple solutions logically and choose the most effective one. Strong analytical skills help in making informed decisions based on facts rather than intuition. Organizations rely on this approach for risk assessment, strategy development, and operational planning
Role of communication and design thinking in decision-making
Effective decision-making requires clear communication to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned and understand the reasoning behind choices. Design thinking enhances this process by incorporating user feedback and iterative improvements. When combined, these approaches help in making well-rounded decisions that consider diverse perspectives. Encouraging open discussions and collaborative input leads to better problem-solving and innovation
Section 5 - Mindset change
A mindset that sees challenges, change, and failure as opportunities to learn, grow, and improve. It values effort, resilience, feedback, and a supportive environment for continuous development.
Duration – Approximately 2 Hours

Embrace Challenges
- View challenges as opportunities for growth and development.
- Step outside your comfort zone and seek out new experiences
Embrace Change
- Understand that change is inevitable and can lead to positive growth.
- Be adaptable and open to new situations and perspectives.
Cultivate a Growth Mindset
- Believe that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort and hard work.
- See effort as a path to mastery and continuous learning.
Focus on Learning and Improvement
- Seek and appreciate constructive feedback.
- Learn from mistakes and setbacks, viewing them as opportunities for growth
Develop Resilience
- Understand that setbacks are temporary and that persistence will lead to improvement.
- Don’t be afraid to try again after failures, and learn from them.
- Find inspiration in the success of others and be motivated to achieve your goals
Embrace Failure as a Learning Opportunity
- Replace the word “failing” with the word “learning”.
- View failure as a chance to understand what went wrong and how to improve.
- Learn from the mistakes of others as well as your own.
Cultivate a Growth-Oriented Environment
- Surround yourself with people who inspire growth and encourage learning.
- Create a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- Promote a positive and supportive environment where mistakes are viewed as learning opportunities.
Key Objectives
Nature of Activities
- Classroom training on cognitive and interpersonal skills
- Orientation on Business Excellence, QMS, Lean, Operations Management, EMS, Financial Planning, etc
- Industry-focused training programs
- Interactive sessions between students and business experts
Training Methodology
- Classroom Training
- Group Dynamics
- Self-Reflection
- Video Analysis
- Group Interventions
- Feedback Discussions with Experts
